
Overview: New GOST R 70747-2023 Standard for Laminated Timber in Building Construction by Timber Expert
New GOST R 70747-2023 Standard for Laminated Timber in Building Construction: A Comprehensive Review
The onset of June 2023 marked a crucial development in Russia's construction industry as it saw the introduction of GOST R 70747-2023 "Laminated timber for walls of buildings. Technical Conditions". This new national standard, approved by the order of Rosstandart on May 18, 2023, under the order number 331-st, has been enforced since June 1, 2023. Aiming to regulate the production of laminated softwood lumber for building walls, it sets forth an array of stipulations for its manufacture at specialized enterprises.
The standard specifically applies to glued laminated softwood lumber, excluding solid wood lumber, profiled lumber, multilayer laminated veneer lumber, and laminated lumber intended for interior fittings like flooring, doors, windows, window sills, mouldings, etc.
Classification of Glued Laminated Lumber
The standard categorizes glued laminated lumber into four distinct types, providing a systematic classification based on their design and characteristics:
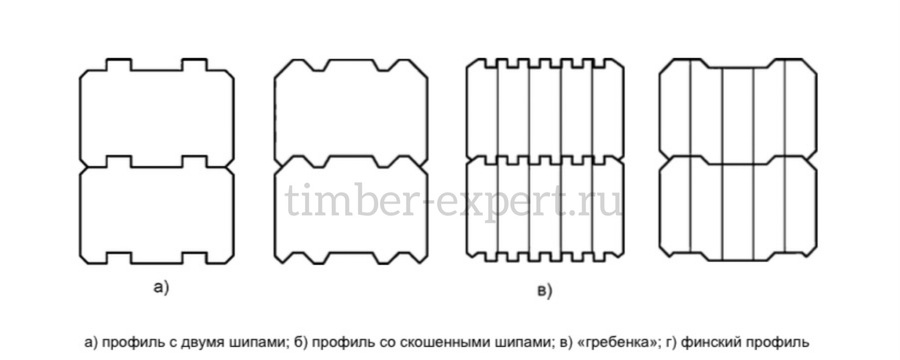
Two studs (2SH)
Bevelled studs (BSH)
Tongue and groove (Gr)
Finnish profile (FP)
Classification of Glued Laminated Lumber By Type of Lamination
The standard further distinguishes laminated wood blocks based on the number of splices they have. Here, we find two variants:
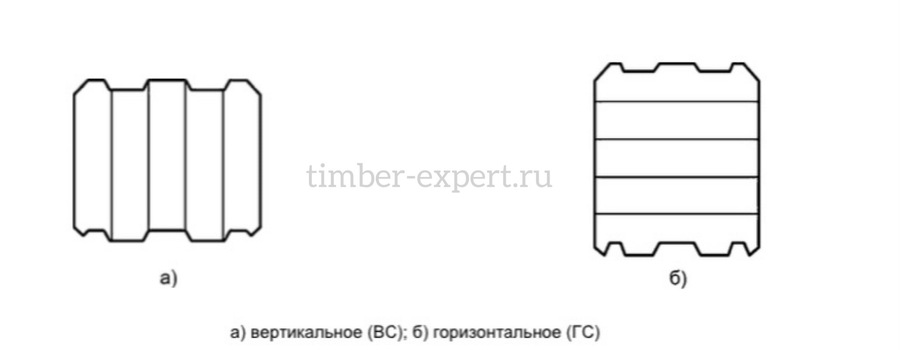
Glued laminated lumber, or glulam, can be classified based on the orientation in which its layers are glued together. This classification gives us two primary types:
Vertical Lamination (VC): In vertical lamination, the layers of the lumber are glued together in a vertical orientation. This means that the grain of the wood runs vertically through the layers, creating a structure that is particularly strong against vertical and compressive forces. It's often used in applications where vertical load-bearing capacity is a crucial factor.
Horizontal Lamination (HC): On the other hand, horizontal lamination involves gluing the layers of the lumber together in a horizontal orientation. Here, the grain of the wood runs horizontally across the layers. This type of lamination is exceptionally strong against bending forces and is typically used in beams, headers, and other elements where resistance to bending stress is required. Both of these types have their unique advantages and are utilized in different structural applications depending upon the specific requirements of the construction project.
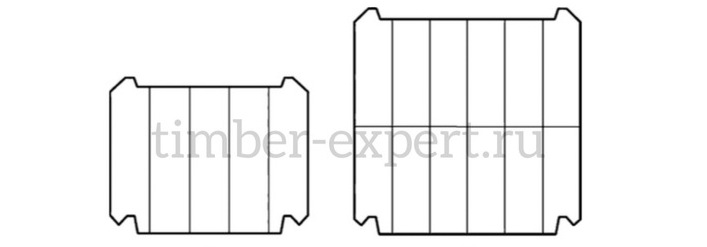
Glued laminated timber can be classified by the number of glued blocks. This yields two primary types:
Single-Story (B1): This type of laminated timber consists of one glued block along the height of the board. This configuration results in a single, continuous piece of laminated timber along the length of the structure.
Double-Story (B2): In contrast, double-story laminated timber is made up of two glued blocks along the height of the board. This type of laminated timber is essentially a high beam that consists of two blocks of laminated timber stacked on top of one another.
These classifications are important as they can influence the strength, rigidity, and other physical properties of the laminated timber. As a result, they play a crucial role in determining the suitability of the timber for various construction applications.
Technical Specifications: A Focus on Raw Materials
The GOST R 70747-2023 goes into considerable detail regarding the technical requirements of the raw materials. These encompass specifications for the wood and adhesive materials that are used, along with rules of acceptance, highlighting the properties that must be determined in the acceptance and periodic tests, as listed in Table 4.
1. Requirements for Wood
The wood, forming the primary component of the laminated lumber, should conform to specific quality standards and be sustainably sourced. The standard might also define the preferred species of trees and their maturity.
2. Requirements for Adhesive Materials
Given the critical role of adhesives in the strength and durability of laminated timber, the standard mandates the use of high-grade adhesive materials. It may stipulate the chemical composition, viscosity, curing time, and other relevant characteristics of the adhesives used.
3. Rules of Acceptance
The rules of acceptance specify the assessment criteria for determining the suitability of raw materials and the finished product. They define the physical and mechanical properties that must be evaluated during acceptance and periodic tests.
The standard also prescribes the minimum handling of glued laminated timber during loading, unloading, and installation, ensuring the preservation of its integrity.
Marking, Packaging, Transport, and Storage
To ensure that the laminated timber reaches the end user in optimal condition, GOST R 70747-2023 provides comprehensive guidelines on marking, packaging, transport, and storage. These guidelines are designed to prevent damage and degradation, thereby ensuring the product's longevity.
Manufacturer’s Warranty
The GOST R 70747-2023 necessitates that manufacturers stand by the quality of their products by providing a warranty. This gives end users assurance about the product's reliability and durability while fostering a sense of responsibility among manufacturers.
In essence, GOST R 70747-2023 ushers in a new era of regulation and quality assurance in the use of laminated timber for building construction in Russia. By setting forth rigorous specifications and guidelines, this standard serves to uphold the integrity of the construction industry and safeguard the interests of all stakeholders.
The Ecological Impact of Laminated Timber from Russia's Forests: A Green Revolution in the Construction Industry
In the heart of Russia's sprawling forests, a remarkable development is taking shape - the harvesting of needles for the production of laminated timber. This eco-friendly innovation is not just revolutionizing the construction industry but also playing a pivotal role in combating climate change. Russia's northern timber, rich in sustainable softwoods, is being leveraged to produce a construction material that is green, durable, and highly efficient: laminated timber.
From Forest to Fabrication: A Sustainable Journey
Russia's forests, particularly its vast northern woodlands, are home to an abundance of softwood species, such as pine, spruce, and larch. These trees are renowned for their excellent growth rates, strength, and longevity, making them the ideal resource for the production of laminated timber. Importantly, these trees absorb significant amounts of CO2 during their lifetime, sequestering carbon and releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
When these trees are sustainably harvested, they are replaced with new seedlings, ensuring that the forest continues its essential role as a carbon sink. Meanwhile, the harvested wood is transported to the mill, where it is transformed into laminated timber.
The production process itself is eco-friendly. Wood residues, such as sawdust and offcuts, are often used to generate energy for the production process, further reducing the carbon footprint. Moreover, the adhesives used in the process are chosen for their low environmental impact.
Laminated Timber: The Eco-Friendly Building Material

Laminated timber has several attributes that make it an exceptionally green building material. Firstly, it is durable and long-lasting, meaning that structures built from laminated timber stand for many years, effectively storing the carbon absorbed by the trees during their growth.
Secondly, laminated timber is incredibly efficient to work with, producing less waste compared to traditional building materials like concrete and steel. Furthermore, any waste that is produced can be recycled or used as biofuel, contributing to a circular economy.
Additionally, buildings constructed from laminated timber are highly energy efficient. The natural insulative properties of wood help to reduce the energy needed for heating and cooling, resulting in lower CO2 emissions over the building's lifetime.
Russia's Role in Global Sustainability
By harnessing the potential of its vast northern forests and embracing the production of laminated timber, Russia is positioning itself as a leader in sustainable construction. The use of locally sourced, sustainably harvested softwoods reduces transportation emissions and supports local economies, providing jobs and supporting communities in the region.
Furthermore, Russia's commitment to sustainable forestry and laminated timber production sends a strong signal globally. It demonstrates that economic development and environmental sustainability can go hand-in-hand, offering a blueprint for other nations to follow.
The laminated timber derived from Russia's majestic northern forests is much more than a building material. It represents a beacon of hope in the global fight against climate change, underlining the potential for sustainable industry practices to drive economic growth while protecting and enhancing our precious environment. Embracing such green innovations, we edge closer to a future where construction and sustainability exist in harmony.








